Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
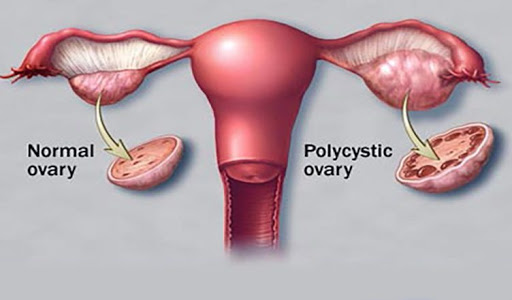
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women during their reproductive years. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms that include irregular menstrual periods, excessive androgen levels, and the development of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS affects approximately 1 in 10 women of childbearing age and can have significant impacts on reproductive health and overall well-being.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person but typically manifest around the time of the first menstrual period. They may include:
- Irregular Periods: Women with PCOS may experience infrequent, prolonged, or unpredictable menstrual cycles.
Polycystic Ovaries: Enlarged ovaries with numerous small fluid-filled cysts containing immature eggs. - Weight gain :Hair loss-Hair on the scalp gets thinner and falls out.
Hirsutism: High levels of androgen hormone can lead to excessive facial and body hair growth, similar to male patterns. - Acne and Skin Issues: Severe acne outbreaks and darkening of skin neck,groin and under the breast are common in women with PCOS due to hormonal imbalances.
male-pattern baldness - Infertility: Difficulty in conceiving due to irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation.
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some contributing factors may include:
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, leading to higher insulin levels. This can stimulate androgen production and disrupt ovulation.
- Hormonal Imbalance: PCOS is associated with abnormal levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and androgens (testosterone).
- Low grade inflammation:women with pcos are low grade inflammationwhich inturn increases androgen production which leads to problems in blood vessels and heart.
- Genetics: A family history of PCOS increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
Complications
PCOS can have several long-term complications, particularly if left untreated. Some potential complications include:
- Infertility: Irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation can make it challenging for women with PCOS to conceive.
- Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension: Women with PCOS have a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes and high blood pressure during pregnancy.
- Metabolic Syndrome: PCOS is linked to an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and unhealthy cholesterol levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance associated with PCOS can lead to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Endometrial Cancer: Irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances can cause the uterine lining to thicken, increasing the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosing PCOS involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Pelvic Exam: A physical examination of the reproductive organs to check for any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Hormone level testing to measure androgen, LH, FSH, and other relevant hormones. Additionally, blood tests for glucose and lipid levels may be performed.
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and check for the presence of cysts.
MANAGEMENT
PCOS can be controlled by following proper diet and exercise along with homoeopathic medication.. Here’s a comprehensive guide on the general management of PCOD/PCOS:
- Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial in managing PCOS. Women with PCOS are often insulin resistant, which can lead to weight gain. Excess body weight exacerbates hormonal imbalances and can make PCOS symptoms worse. Aim for a BMI within the range of 18.5 – 24.9. If you are overweight or obese, even a modest weight loss of 5 to 10 percent can have a positive impact on your menstrual cycle and hormone levels.
- Follow a Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet plays a vital role in managing PCOS. Consider the following dietary recommendations:
- Low-Carb Diet: Limiting the consumption of carbohydrates, especially refined sugars and starchy foods, can help regulate insulin levels. Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Healthy Fats: Include healthy fats in your diet, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Protein-Rich Foods: Incorporate lean proteins like fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes into your meals.
- Fiber: A diet high in fiber helps control blood sugar levels and aids in weight management. Include plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains in your diet.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and help with weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, spread over at least five days. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, dancing, or swimming can be beneficial.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen hormonal imbalances. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough restful sleep is essential for hormonal balance and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to insulin resistance. Limit their consumption or avoid them altogether.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbal supplements, like cinnamon, spearmint tea, and fenugreek, have shown potential in managing insulin levels and reducing androgen levels. Consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal supplements.
HOMOEOPATHIC MANAGEMENT
Homeopathy offers an alternative approach to managing PCOS by addressing the root cause of the condition and promoting overall well-being. Homeopathic medicines are chosen based on individual symptoms and the patient’s constitution, aiming to restore hormonal balance and improve metabolic functions. It is essential to consult a qualified homeopathic practitioner for personalized treatment.Some of the commonly used medicines are,
- Apis Mellifica: This remedy is indicated for inflammation of ovaries with severe pain, especially in the right ovary, irregular periods, and suppressed menses. Symptoms are often relieved by cold water and open-air exposure.
- Natrium Muriaticum: Suitable for individuals with weakness and weariness, profuse bleeding during periods, and a desire to support the back. Mental exertion worsens symptoms, and symptoms improve in open air and with cold bathing.
- Sepia Officinalis: Effective for managing hot flashes at menopause, yellow-greenish vaginal discharge with itching, late, scanty, and irregular menses. Nausea on an empty stomach and prolapse of the uterus and vagina can also be alleviated with this remedy.
- Calcarea Carbonica: Useful for individuals with problems due to impaired nutrition, swelling in various glands, and pain in the lower back. Symptoms like white discharge, abdominal pain, and headaches before periods can be managed with this remedy.
- Lachesis Mutus: Particularly helpful at the beginning and end of menses, indicated for inflammation of the breasts, pain and swelling in the left ovary, and sensitivity to tight clothing. Scanty periods and waves of pain in the head can be addressed with this remedy.
- Lycopodium Clavatum: This remedy is beneficial for individuals with delayed menses with profuse bleeding, pain in the right ovarian region, and distended and bloated abdomen. Symptoms worsen in the evening and improve with warm food and drinks.
- Bryonia Alba: Suitable for individuals with early periods with profuse bleeding, stitching and tearing pain in any muscle, and severe pain in the right ovary extending to the thigh.
- Pulsatilla Pratensis: Indicated for women with absence or late periods, clotted and thick menstrual bleeding, and chilliness and nausea during menses. Symptoms worsen with fatty meals and improve in the open air.
Effectiveness of Homeopathic Treatment
Several published research documents indicate the significance of homeopathy in the management of PCOS and its associated symptoms. While individual responses may vary, homeopathy aims to address the underlying imbalances and promote long-term health and well-being.