Understanding Uterine Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Introduction
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus during a woman’s childbearing years. These growths can vary in size, ranging from tiny seedlings to large masses that can significantly distort and enlarge the uterus. While they are not commonly associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer, fibroids can cause various symptoms and complications for some women. In this blog, we will delve into the types, causes, risk factors, symptoms, complications, prevention strategies and homoeopathic management related to uterine fibroids.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
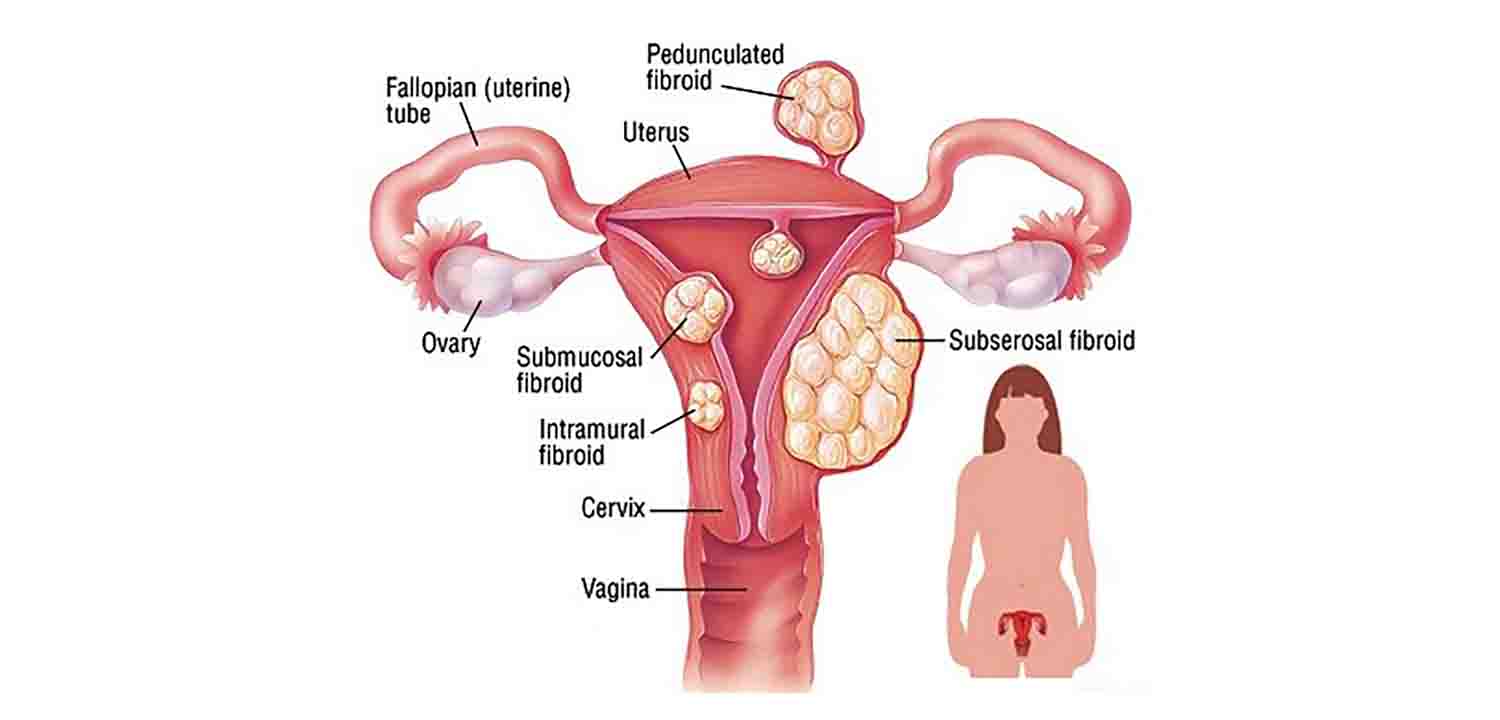
Fibroids are generally classified based on their location within the uterus:
- Intramural Fibroids: These fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall and are the most common type.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Bulging into the uterine cavity, these fibroids can cause heavy menstrual bleeding and fertility issues.
- Subserosal Fibroids: Projecting to the outside of the uterus, these fibroids may cause pelvic pressure and discomfort.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
- Despite extensive research, the exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unknown. However, medical experts have identified several factors that may contribute to their development.
- Genetic Changes: Many fibroids exhibit genetic changes that differ from normal uterine muscle cells.
- Hormones: Hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, play a crucial role in promoting the growth of fibroids. These growths have more estrogen and progesterone receptors than regular uterine muscle cells.
- Other Growth Factors: Substances like insulin-like growth factor may influence fibroid growth.
- Extracellular Matrix (ECM): The presence of increased ECM in fibroids causes them to become fibrous and store growth factors, resulting in biologic changes in the cells themselves.
Risk Factors for Uterine Fibroids
- Age: Fibroids are more common in women during their reproductive years, typically between ages 30 and 50.
- Family History: If a woman has a family history of fibroids, her risk of developing them increases.
- Ethnicity: Studies have shown that women of African descent are more likely to develop fibroids compared to women of other ethnic backgrounds.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk of fibroid development.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
While many women with fibroids remain asymptomatic, those who do experience symptoms may have the following:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Prolonged and heavy periods, sometimes lasting more than a week.
- Pelvic Pressure or Pain: A sensation of fullness or discomfort in the pelvic region.
- Frequent Urination: Increased urge to urinate due to fibroids pressing on the bladder.
- Difficulty Emptying the Bladder: Fibroids can obstruct the bladder, leading to difficulty in emptying it completely.
- Constipation: Large fibroids may put pressure on the intestines, causing constipation.
- Backache or Leg Pains: Fibroids can exert pressure on surrounding nerves, leading to back and leg pain.
Complications Associated with Fibroids
In rare cases, fibroids can lead to complications.
- Acute Pain: Fibroids may cause sudden and severe pain if they outgrow their blood supply and begin to die.
- Infertility: Submucosal fibroids can interfere with implantation and lead to fertility issues.
- Pregnancy Complications: Large fibroids may increase the risk of certain pregnancy complications, such as placental abruption, fetal growth restriction, and preterm delivery.
Prevention and Management
While preventing uterine fibroids entirely may not be possible, women can adopt healthy lifestyle choices to manage their risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being at a healthy weight reduces the risk of fibroids.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate fruits and vegetables into your diet to potentially decrease your fibroid risk.
HOMOEOPATHIC MANAGEMENT
Homoeopathic remedies can manage small fibroids very well;however large fibroids need surgery.Medicines are selected based on the person’s physical, and mental symptoms, as well as their overall constitution.
Here’s the list of homeopathic medicines for uterine fibroids, considering the patient as a whole:
1.Thlaspi Bursa Pastoris
- Indicated for uterine fibroids with prolonged menses.
- Suited to individuals who experience menses for 10-15 days, appearing very frequently.
- Menstrual bleeding is profuse, with the presence of large clots.
- Violent uterine colic during menses may also arise.
- Patients may exhibit emotional sensitivity and restlessness.
2. Calcarea Carb
- Useful for treating heavy periods from uterine fibroids.
- Suited to individuals with a tendency to gain weight and feel chilly.
- Menses continue for a long time and may appear early.
- Vertigo during menses may arise.
- Leucorrhea of thick, milky, or yellow color may be present.
- Patients may be anxious, overworked, and have a fear of failure.
3. Belladonna
- Indicated for painful menses in uterine fibroids.
- Suited to individuals with sudden, intense symptoms.
- Cramping pain in the uterus during menses.
Menses are bright red and profuse. - Patients may have a flushed face, be irritable, and have difficulty sleeping.
4. Sepia Officinalis
- Recommended for griping, burning, or bearing down pains during menses.
- Suited to individuals who feel overwhelmed and emotionally distant.
- Menses start early and are quite copious.
- Fainting and chilliness during menses may attend.
- Also indicated for painful intercourse in uterine fibroids cases.
5. Ustilago Maydis
- Suitable for uterine fibroids with dark menstrual bleeding.
- Suited to individuals who feel sensitive and easily offended.
- Menstrual bleeding may contain clots and have a stringy nature.
- Patients may experience mood swings and weepiness.
6.Sabina Officinalis
- Significant medicine for menstrual bleeding with clots in uterine fibroid cases.
- Suited to individuals who are sensitive and easily irritated.
- Menstrual bleeding worsens with the slightest motion.
- Pain from sacrum to pubis, which improves by lying on the back.
- Uterine pain may extend to the thighs.
- Other symptoms include foul, acrid, corrosive, yellow leucorrhea.
7. Fraxinus Americana
- Excellent medicine for uterine fibroids with a bearing down sensation in the pelvis.
- Suited to individuals who feel weak and debilitated.
- Patients may experience a sensation of pressure in the pelvic region
8. Trillium Pendulum
- Recommended for uterine fibroids with back pain during menses.
- Suited to individuals who experience weakness and fatigue.
- Back pain may radiate to the hips during menses.
- Tight binding of the back and hips provides relief.
- Menstrual bleeding is bright red and gushing.
- Faintness from uterine bleeding may be present.
- Also indicated for inter-menstrual bleeding every two weeks.
9. Kali Carbonicum
- Selected when there is violent back pain during menses.
- Suited to individuals who are responsible and hardworking but tend to become anxious and overwhelmed.
- Pain gets better from sitting and pressure.
- Menstrual flow is copious.
10. Erigeron Canadensis
- Beneficial for treating frequent urination in case of uterine fibroids.
- Suited to individuals who may be restless and excitable.
- Painful urination may also arise.
- Excessive menstrual bleeding with bright red color may be present.
- Also used for inter-menstrual bleeding from slight exertion.
11. China Officinalis
- Effective for uterine fibroids with heavy bleeding and anaemia.
- Suited to individuals who feel weak and exhausted from loss of fluids.
- Profuse, dark menstrual bleeding with clots.
- Exhaustion and fainting spells may arise.
12. Ferrum Met
- Indicated when menses are pale, watery, heavy, and prolonged leading to anaemia.
- Suited to individuals who are usually strong but become weak and pale during menses.
- Menstrual flow worsens with the slightest movement.
- Lower back or abdomen pain during menses may be observed.
- Keep in mind that the selection of the right homeopathic remedy requires a thorough understanding of the patient’s unique symptoms, temperament, and constitution. It’s essential to consult a qualified homeopath for personalized treatment and guidance.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are common noncancerous growths that affect many women during their reproductive years. While the exact cause remains unclear, hormonal factors and genetic changes play significant roles in their development. Although fibroids may not always cause symptoms or complications, those experiencing issues should seek medical attention promptly. By understanding the risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle, women can take proactive steps to manage their fibroid risk and overall reproductive health. aSmall fibroids can be managed by homoeoepathic medicines.
Note: Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment options.